Ohio Mitigation License # RC202
- What is Radon?
- Important Facts About Radon
Learn critical facts about Radon Gas including how it enters a home, how it interacts with the human body, which states are at risk and more.
Radon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment by seeping out of rocks and soil. Radon comes from the depletion of uranium that has been in the ground since Earth's formation.

Radon flows from the soil into outdoor air and into the air in homes and commercial buildings from the movement of gases in the soil beneath the structure.
Outside air typically contains extremely low levels of radon, but it builds up in larger concentrations inside a building when the gas is unable to disperse
Unlike better-known home hazards like asbestos and lead-based paint, many people are unaware of the danger of household radon exposure because the gas is odorless, tasteless and colorless.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that 1 of 15 homes in the United States and as many as 1 of 3 homes in some states about 7 million homes have high radon levels.
So you might be asking how does Radon cause so many problems?
Here's the deal.
Radon is a chemically inert gas that is electrically uncharged but it is also radioactive, and it is this fact, that creates the potential for trouble.
You don't have to be a nuclear engineer to understand that radioactive materials decay spontaneously, we should have all learned that in a basic chemistry class, however, within this decay process, radon progeny are formed which do carry an electric charge, this allows them to bind to tiny dust particles in the air, which can be inhaled by the lungs and adhere to the lining of your lung tissue.
These deposited atoms decay within the lung tissue by emitting a type of radiation called, alpha radiation, which holds the power to damage cells in the lung and mutate the structure of your DNA. This can start a chain reaction process that can lead to lung cancer.
According to the study on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation, 1 in 10 of all lung-cancer deaths in the United States; which amounts to a number between 15,400 to 21,800 per year, can be attributed to radon.
Radon in the US is measured in PicoCuries per Liter.
The EPA recommends that action is taken on any home recording radon levels between 2-4pCi/L and above.
The World Health Organizations recommends that measures should be taken on any home producing radon levels at or above 2.7 pCi/L.
There are two types of devices for measurement:
1. Passive devices are ones that do not need power to function.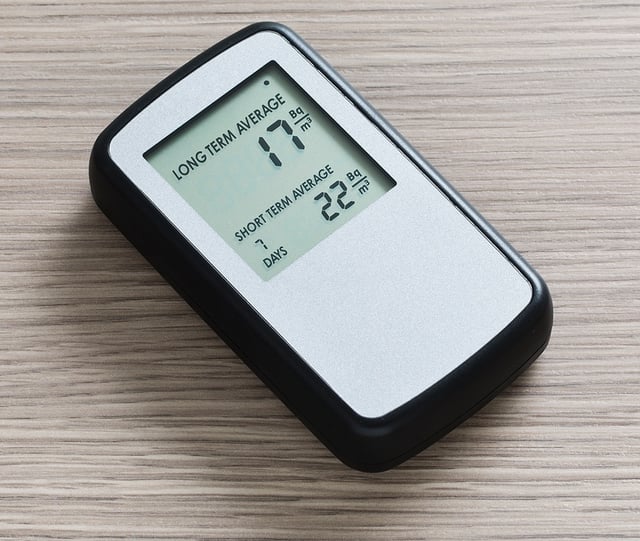
The group includes alpha track detectors, charcoal canisters, and charcoal liquid scintillation detectors.
They are sometimes available in drug, hardware, and other stores, the Internet, and through some laboratories.
These test kits are designed to be used for two or four days before being returned for analysis by the laboratory that provides it. A return mailer is provided with the kit.
One thing to keep in mind, some of the charcoal technologies are prone to interference by high humidity, so may not be appropriate for use in all buildings.
2. Active devices require power to function.
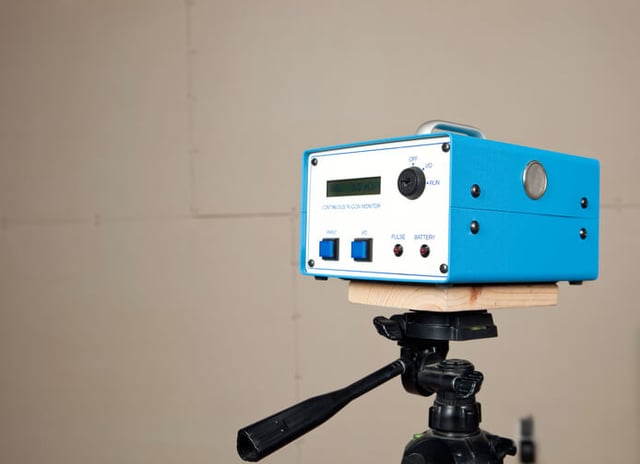

This group of radon testing devices consists of different types of continuous monitors and continuous working level monitors.
Active monitors can provide data on the range of variation within a given test period. Some are designed to detect and deter interference. These tests often cost more than passive testing but are typically more accurate due to the degree of sophistication with this technology itself
The electronic continuous radon monitor is set on a tripod and is designed to precisely measure (with 99.9% certainty) the actual radon levels in a house for 52 hours.
There are four common factors that could influence the results of a radon test so make sure they are accounted for during the test:
In addition to the four influences above, if you have your home professionally tested, make sure that the Radon testing company has a national accreditation such as the American Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists (AARST)
According to the World Health Organization, Radon primarily enters homes through the following areas:
Radon levels are usually higher in basements, cellars or living spaces in contact with soil, this is also why it is the preferred area to test radon levels within a home.
Another concept to keep in mind is that the total concentration of radon can vary from home to home. Residential radon tests on air quality indicate that homes adjacent to one another can have a high degree of variance between total radon levels, thus rendering one home safe and another a serious health risk.
Total concentration of radon in a home depends on a few factors including:
Well, to be perfectly honest, you really can never get rid of radon, radon breaks down over time so you can't wave a magic wand and say bye bye, what you can do is make sure you limit the total amount that is able to get into your home, this is done through a process called radon mitigation.
With that being said,
Let's look at the 2 different types of Radon Mitigation Systems you can have installed.
A passive radon mitigation system is typically installed when a home is being constructed.
The passive system contains only two components:
A passive system relies on natural pressure differentials and air currents to eliminate radon from the home.
Oftentimes when a home is being built, the building company will install a passive system without ever testing the home for radon.
This can be a problem because passive radon systems do not bring extremely high levels of radon below the EPA recommended 4.0.
Many home buyers do not realize this when purchasing a home with a passive system, but they might be putting their family's health at risk.
 An active radon mitigation system is installed when homes contain elevated levels of radon gas.
An active radon mitigation system is installed when homes contain elevated levels of radon gas.
It is referred to as an active system because the fan is always pulling radon from beneath the home, so it doesn't have the opportunity to enter and venting it outside. This is referred to as the sub-slab depressurization method.
The active system has four components:
There are several ways for an active mitigation system to be installed depending on the layout of the home, this includes crawlspaces, the overall size of the home, the current radon level, the composition of your soil and more.
The majority of active radon removal systems can be installed in just a few hours, depending on the complexity of the home.
An EPA certified crew should always walk you through the process of radon removal including, how the piping and fan are going to be installed to ensure radon is being removed if the most efficient and effective manner. The average radon mitigation system can be installed for under $1,500. Every home is built a little differently, and therefore, there is no universal price for every home.
Radon can be found in any state but there are certain states that are at a much higher risk.
Radon Zones can be found at the EPA website here
High radon areas in the U.S. tend to be in the northern section of the country due to the types of soils found there. Most of all of these states fall in zone one, as detailed in the map above, which are designated for parts of the U.S. with the highest levels of radon ie. 4 (pCi/L) or higher.

Features that reduce household radon levels can be incorporated into new homes. In fact, eleven states now require radon-resistant features in new homes. Every home should be tested before, or soon after, you move in.
Even homes built with radon-resistant construction features need to be tested for the safety of the occupants. If high radon levels are found, it is easier and costs less to reduce radon levels in homes that are built radon-resistant.
Using common construction materials and easy to follow techniques, builders can provide a public health service by constructing new homes that are resistant to radon entry, therefore, helping to reduce a buyers' risk of lung cancer.
According to the EPA for Radon Resistant Construction,
Radon Eliminator
4392 S. Arlington Rd
Uniontown, OH 44685
Call Us: 330-248-5322